Section outline
-
-
What is waste?
The understanding of waste is different from places to individuals to society. But, it is common issue which requires immediate action. The level of understanding the concept and fundamentals of waste is an important for the sustainable management of waste. The following session will define the terminologies of waste and management.
As per the international Organizations like:
United Nations Statistics Division, as per Glossary of Environment Statistics, “wastes as materials that are not prime products (that is, products produced for the market) for which the generator has no further use in terms of his/her own purpose of production, transformation or consumptions, and of which she/he wants to dispose. Waste may be generated during the extraction of raw materials, the processing of raw materials into intermediate and final products, the consumption of final products, and other human activities,. Residuals recycled or reused at the place of generation are excluded.”

-
-
-
Waste Disposal
Historically, efforts in the management of waste have focused primarily on the disposal part of the waste management. Whilst local governments are now moving towards recovery of resources from waste, disposal is still the most common form of managing waste, including open dumping, landfilling of waste and incineration. In developing countries, infrastructure for waste management may be limited, and waste is often left uncollected or disposed of in inappropriate locations, leading to significant environmental and public health problems.
For example, in India, the Yamuna river, which flows through Delhi, is heavily polluted due to the dumping of untreated waste and sewage. In Nairobi, Kenya, the Dandora landfill site, which was opened in the 1970s, has become a symbol of environmental degradation and pollution due to the lack of proper management and regulation.
Landfilling of waste is also carried out in places where land is available. In many cases, these landfills are unfortunately poorly designed and operated, resulting in environmental pollution and health hazards for the communities living near them. For example, in the Philippines, the Payatas landfill in Quezon City, Manila, is one of the largest landfills in the country, but it is also notorious for the large number of waste-related accidents and illnesses that occur in the area.
-
-
-
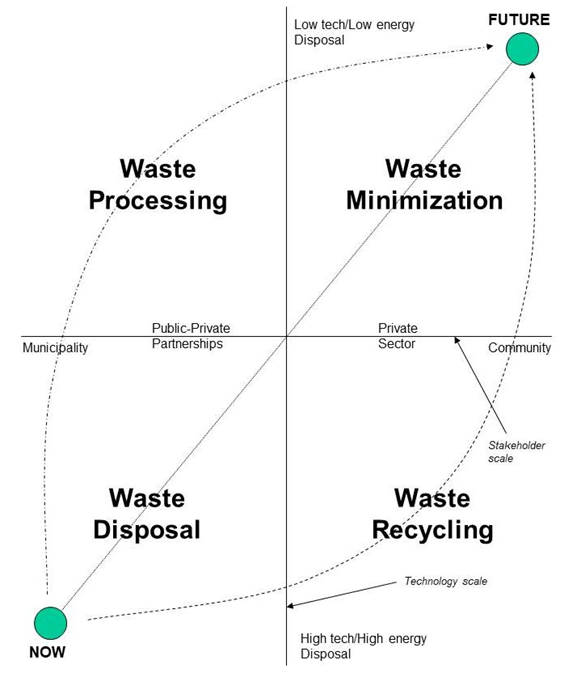
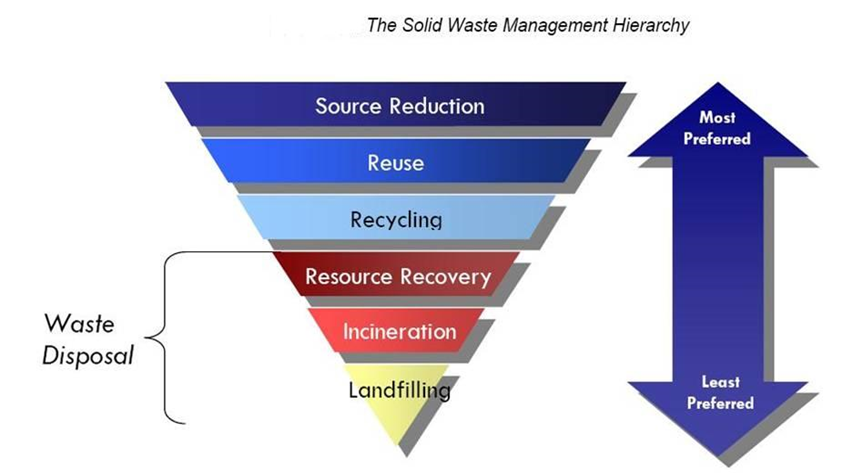
Three components of waste management:
1. Source reduction, or reducing the amount of waste entering the waste stream, is best.
2. Recovery (recycling and composting) is next best.
3. Disposal is the least desired option.
-
-
-
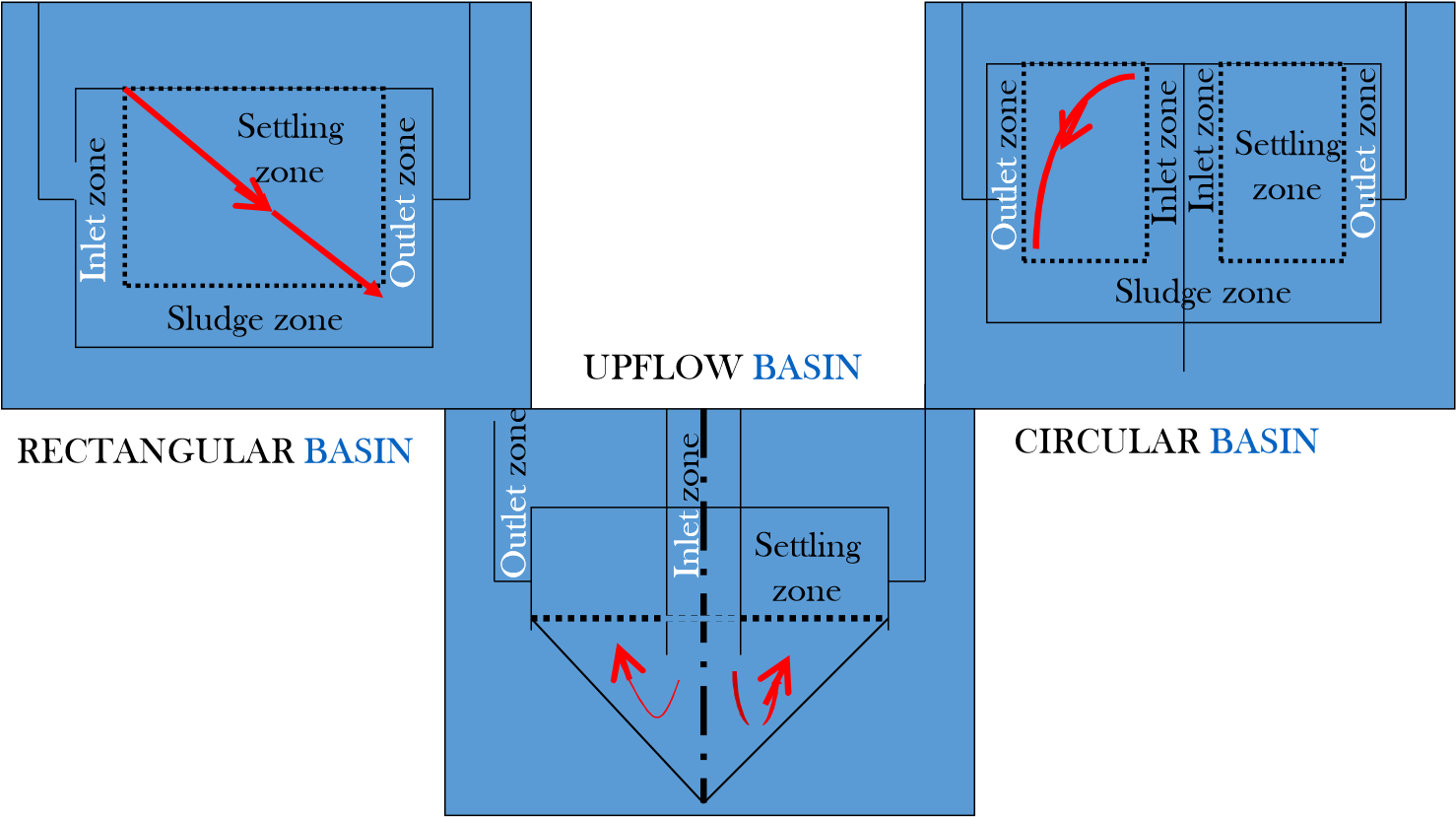
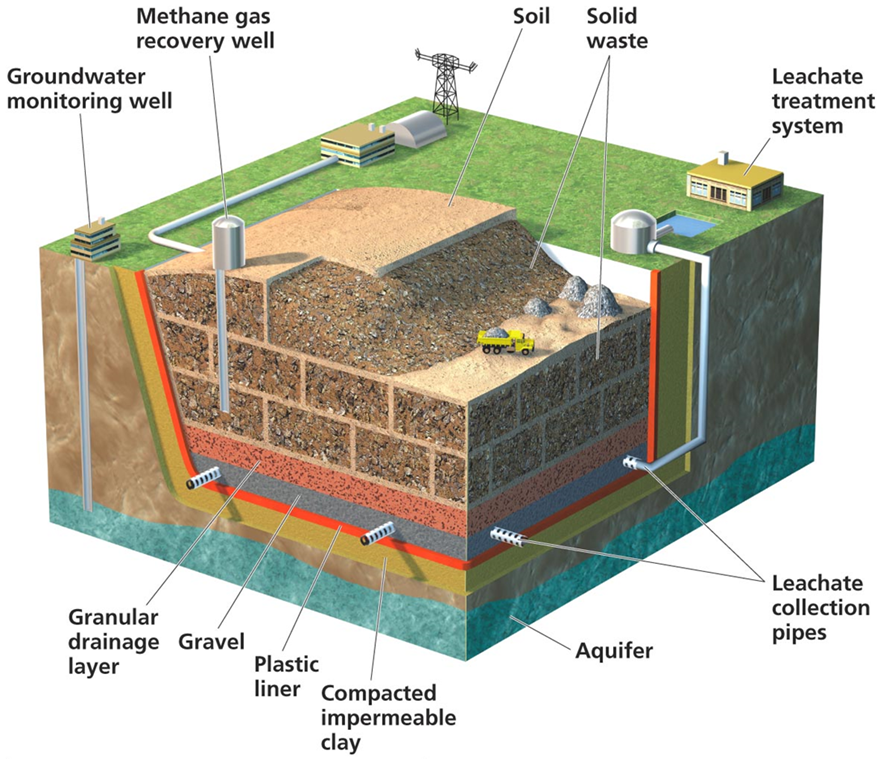
Landfill
A landfill site is a location that has been prepared for the purpose of dumping waste, rubbish or debris. Before the land is used to store waste, diggers are used to give it a suitable shape and it is covered with an artificial water-resistant coating to prevent the rubbish from contaminating the soil. The law states that landfill sites must be located away from inhabited areas, as well as areas used for farming or drinking water.
-
-
-
Hazardous waste: Disposal methods
Landfills: Special landfills with stricter regulations are used for hazardous waste.
Surface impoundments: Ponds lined with plastic and clay. Liquid hazardous waste evaporates, leaving residue.
Deep-well injection: Hazardous waste is pumped deep underground into porous and stable rock formations, away from aquifers.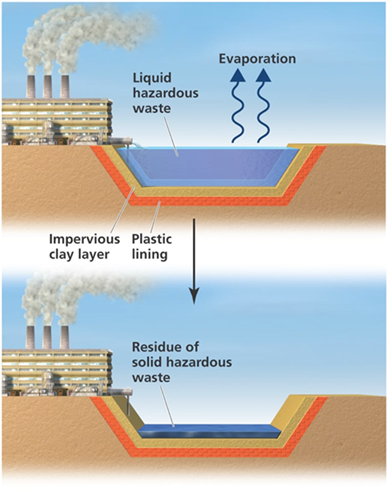
-
-
-
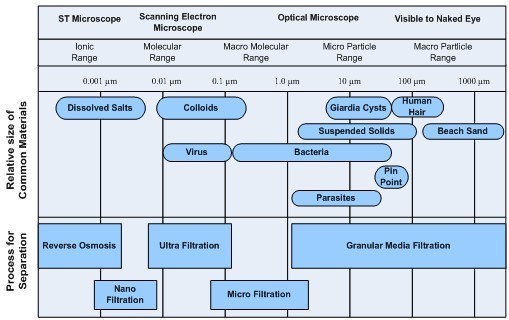
Industrial wastewater is the aqueous discard that results from substances having been dissolved or suspended in water, typically during the use of water in an industrial manufacturing process or the cleaning activities that take place along with that process.
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment.
-
-
-
-
Opened: Wednesday, 1 November 2023, 12:00 AMDue: Friday, 3 November 2023, 11:00 PM
Submit your homework handwritten pdf
-
-
-
-
Opened: Friday, 24 November 2023, 12:00 AMDue: Friday, 1 December 2023, 12:00 AM
Please add Google drive link in a doc file and submit the file, also include your group members id in the doc.
-