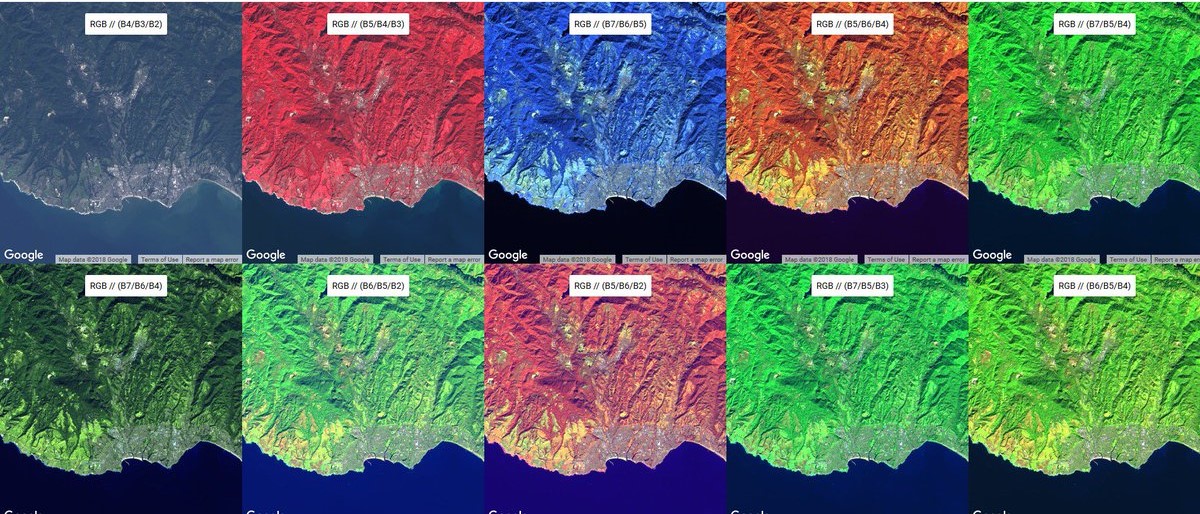
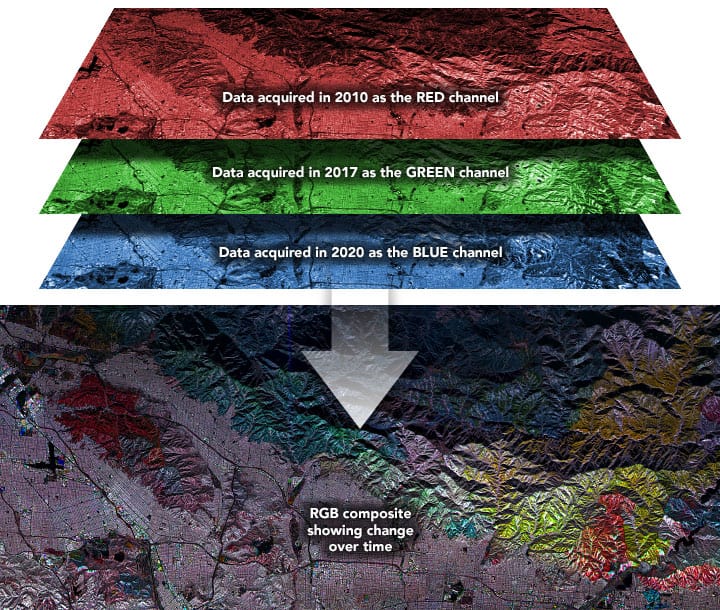
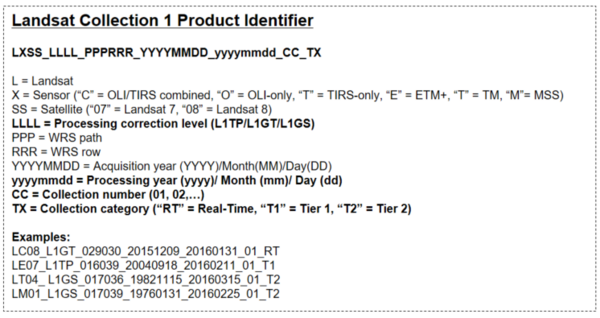
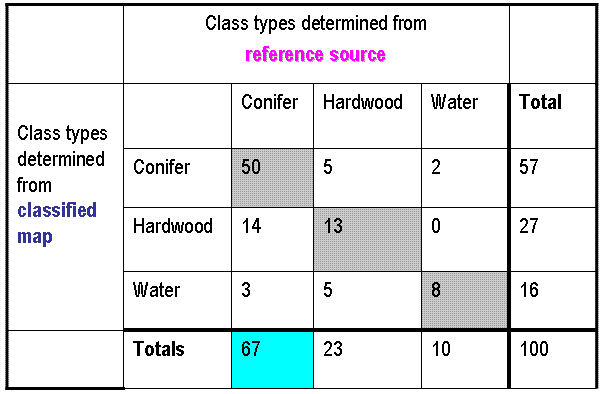
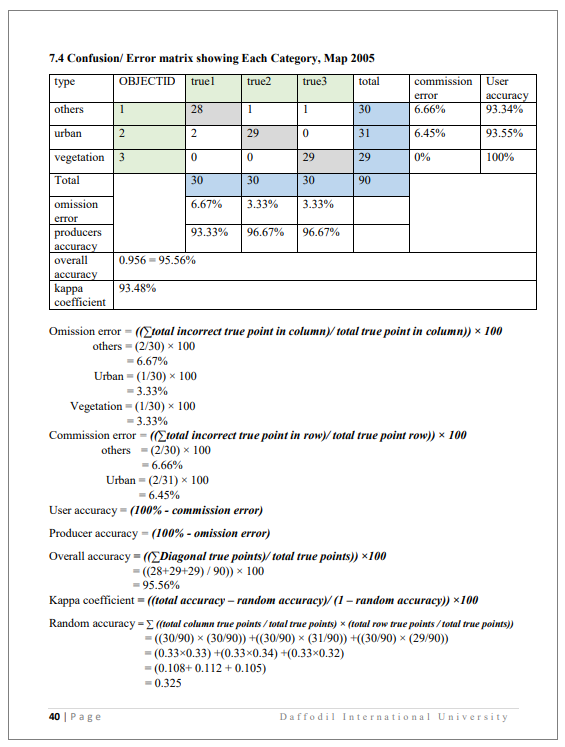
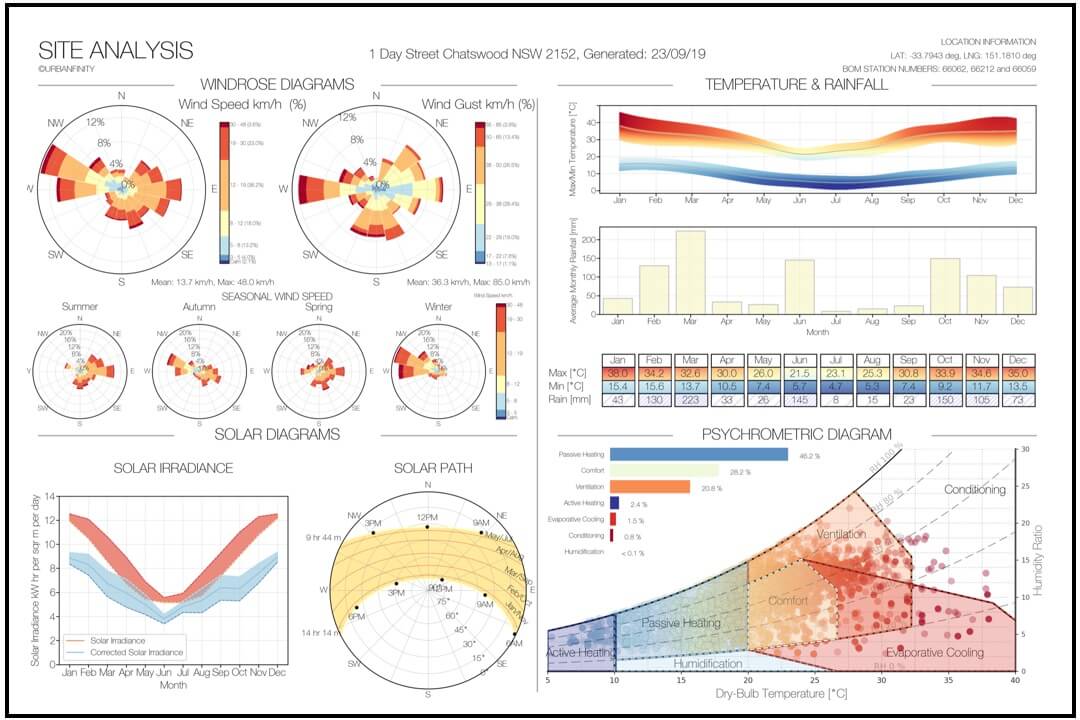
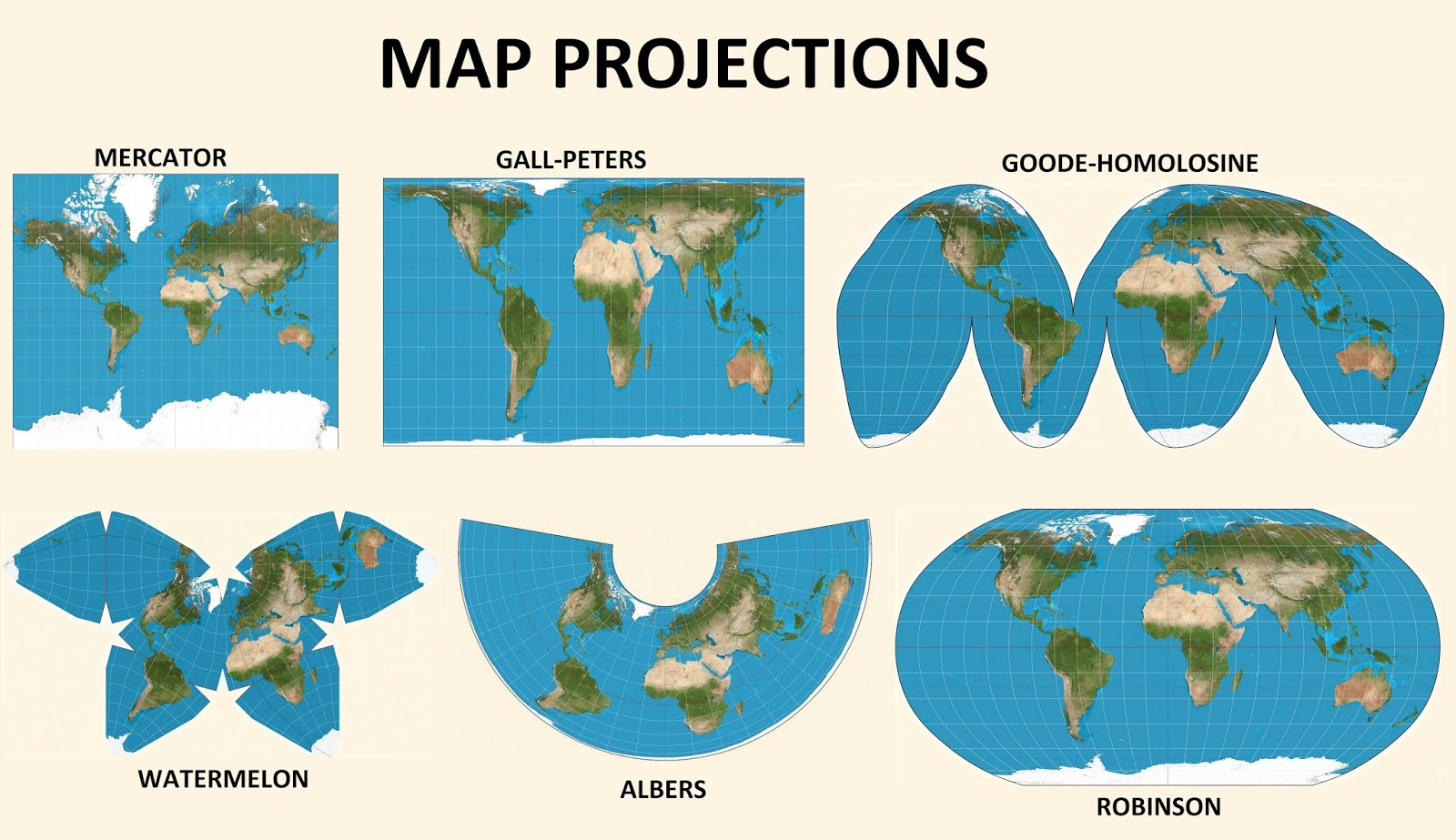
Remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance (typically from satellite or aircraft). Special cameras collect remotely sensed images, which help researchers "sense" things about the Earth. Some examples are:
- Cameras on satellites and airplanes take images of large areas on the Earth's surface, allowing us to see much more than we can see when standing on the ground.
- Sonar systems on ships can be used to create images of the ocean floor without needing to travel to the bottom of the ocean.
- Cameras on satellites can be used to make images of temperature changes in the oceans.
Some specific uses of remotely sensed images of the Earth include:
- Large forest fires can be mapped from space, allowing rangers to see a much larger area than from the ground.
- Tracking clouds to help predict the weather or watching erupting volcanoes, and help watching for dust storms.
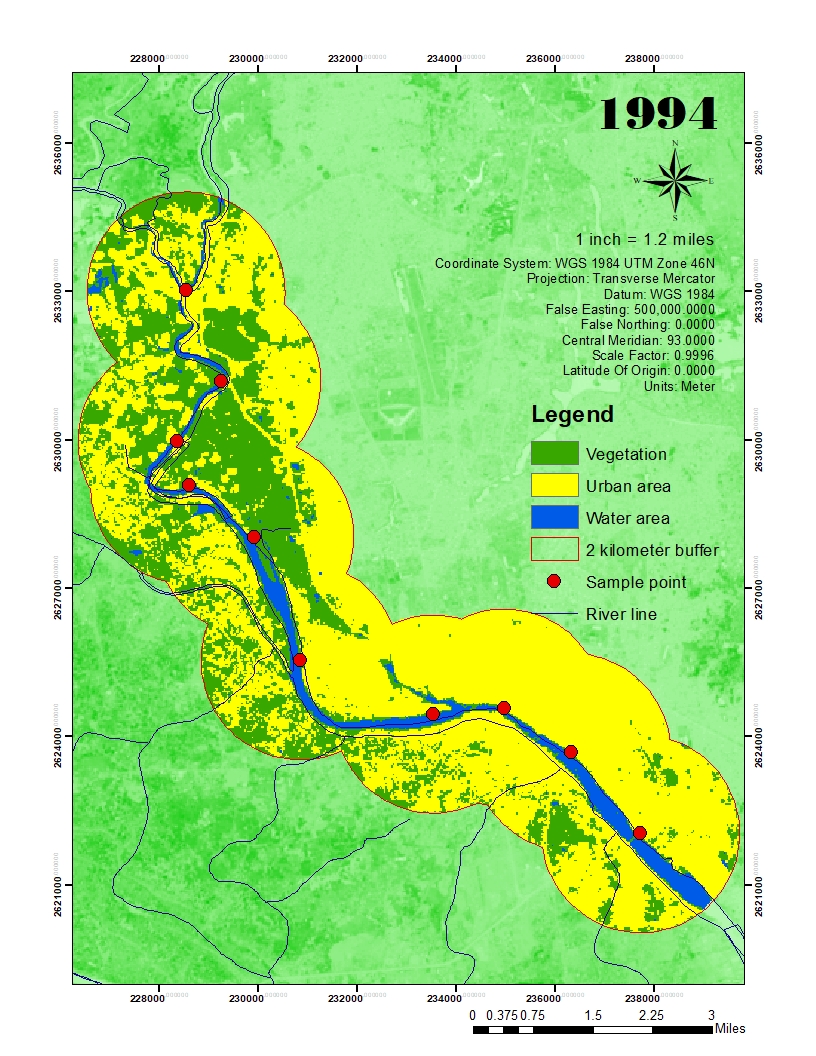
- Tracking the growth of a city and changes in farmland or forests over several years or decades.
- Discovery and mapping of the rugged topography of the ocean floor (e.g., huge mountain ranges, deep canyons, and the “magnetic striping” on the ocean floor).