Section outline
-
-

- Md.
Robin Khan
- Lecturer
- Department
of Pharmacy
- Cell: 01794395481
- Email: robin.ph@diu.edu.bd
- For more information please visit the following link: https://sites.google.com/diu.edu.bd/mdrobinkhan/home
- Md.
Robin Khan
-
-
This subject deals with the knowledge of microorganisms which make the students competent for the microbiological department of the pharmaceutical industry as well as research.
Course contents:
1. Introduction to microbiology: Microbiology as a field of biology, place of microorganisms in the living field, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, protists, groups of microorganisms, areas of microbiology, application of microbiology.
2. History and evolution of microbiology: Spontaneous generation and biogenesis, germs theory of diseases, pure culture concept, immunization, widening horizons.
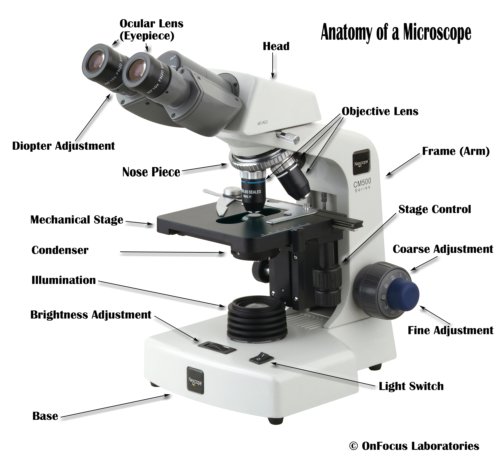
3. Microscopic observations of microorganisms: Bright field, dark field, fluorescence and phase contrast microscopy, electron microscopy, preparations of microscopic examinations, wet mount and hanging drop techniques, fixed and stained smears, microbiological stains, simple and differential staining methods.
4.Bacteria: Nomenclature of bacteria, morphology and fine structures, nutritional requirements, bacteriological media, growth and reproduction, quantitative measurement of bacterial growth, maintenance and prevention of pure culture of bacteria, bacterial infection.
5.Yeasts: types, morphology, reproduction and physiology, pathogenic yeasts.
6.Rickettsiae: Introduction, characteristics of rickettsiae, pathogenic rickettsiae, laboratory diagnosis of rickettsial diseases.
7.Viruses: Virus inhibition, human and animal viruses, control of viral infections, bacterial virus or
bacteriophages, morphology and composition, cultivation of bacterial viruses, reproduction of bacterial viruses.
8.Basic concepts of immunology: Infections, pathogenicity and virulence, immunity.
Course learning objectives:
- Identify and describe the basic principles of pharmaceutical microbiology
- Participate in microbiological risk assessments for pharmaceutical and food products
- Develop expertise in identification, cultivation and counting of microorganisms, preparation
- and sterilization of bacterial culture, various staining techniques, aseptic processing etc.
- Apply their knowledge for research and development of antimicrobial agents
Teaching Strategy:
- Lecture,
- Discussion,
- Demonstration
- Brainstorming,
- Case Studies,
- Problem-based Learning (PBL)
- project
- Video clips,
- Cooperative Learning
Assessment strategy:
Class attendance: 5, Quiz: 10, Assignment: 5, Presentation: 5, Midterm: 25, Semester final: 50; Total = 100
Grading System:
Numerical grade
Letter Grade
Grade Point
80% and above
A+
A Plus
4.0
75% to less than 80%
A
A Regular
3.75
70% to less than 75%
A-
A Minus
3.5
65% to less than 70%
B+
B Plus
3.25
60% to less than 65%
B
B Regular
3.0
55% to less than 60%
B-
B Minus
2.75
50% to less than 55%
C+
C Plus
2.5
45% to less than 50%
C
C Regular
2.25
40% to less than 45%
D
D Regular
2.0
Less than 40%
F
Fail
0.0
-
- Microbiology- Michael J. Pelczar, Noel R. Kreig and E.C.S Chan. 5th edition, Tata Mc Graw Hill Publishing Company Limited, New Delhi.
- Microbiology: An Introduction- Tortora, BerdellR.Funkee& Case, 8th edition, Prentice-Hall.
- Biology of Microorganisms- TD Brock, MT Madigan, JM Martinko, and J. Parker, 7th edition, Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
- Prescott and Dunn’s Industrial Microbiology- Samuel Cate Prescott, Cecil Gordon Dunn and Gerald Reed, 4th edition, Chapman & Hall.
- Pharmaceutical Microbiology- Harris. Fundamental Principles of Bacteriology- A.J. Salle, 7th edition, Mc Graw Hill Book Company
-

Instruction/Guideline for the course:
All the students registered for this course have to enroll in Moodle.
Students can find all the course materials from Moodle.
All the students have to submit the soft copy of their "Assignment" in Moodle under the assignment section created here and for this, they will be graded here.
One Question and Answer forum is created under each of the chapters. Students have to ask their question on this forum and marks will be given for their feedback
Also there is a interactive quiz after each chapter. Students have to take it before moving towards next chapter.
Any announcement regarding the class will be posted on Moodle. So they have to keep themselves always active on Moodle.
All the quizzes and presentations will be held on online (Moodle) and maybe a few of the class will be held on the face to face class and it will be announced before the class.
The question pattern and the syllabus for the quizzes, midterm, and the final exam is given hereunder each of the section (quizzes, midterm, and final).
-
Lecture Contents:
- Microbiology as a field of biology
- place of microorganisms in the living field
- prokaryotic and eukaryotic, protists
- groups of microorganisms
- areas of microbiology
- application of microbiology.
Learning outcomes of this topic:
- Categorize the basic terminology of microbiology
- Compare and Contrast between different cells.
- Predict applications of different methodologies in different pharmaceutical fields.
- Justify the application of microbiology.
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

Lecture Contents:
- Spontaneous generation and biogenesis
- germs theory of diseases
- pure culture concept
- immunization, widening horizons.
Learning outcomes:
- Describe the concept of microbiology
- Analyze different theories for evolution of Microbiology.
- Prepare different culture media for microbial growth.
- Identify vaccination for different disease.
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

Lecture Contents:
- Bright field, dark field, fluorescence and phase contrast microscopy
- electron microscope
- preparations of microscopic examinations
- wet mount and hanging drop techniques
- fixed and stained smears
- microbiological stains
- simple and differential staining methods.
Lecture outcomes:
- Describe different parts and function of different types of microscope
- Compare and contrast between techniques for microbial observations
- Differentiate between different bacterial cells
- Apply the knowledge during research.
- Prepare sample for microscopic observations
- Choose the best techniques of microscopy for pharmaceutical research
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-
Lecture Contents:
- Nomenclature of bacteria
- morphology and fine structures
- nutritional requirements
- bacteriological media
- growth and reproduction
- quantitative measurement of bacterial growth
- maintenance and prevention of pure culture of bacteria
- bacterial infection.
Lecture outcomes:
- List different types of bacteria according to their morphology and characteristics
- Describe the bacterial growth and reproduction.
- Describe the maintenance and preservation process of bacteria
- Identify different nutrients for bacterial growth
- Analyze different types of bacterial infection.
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

- The topic of assignment will be informed later
- The topic of assignment will be informed later
-

Midterm Exam includes: Lecture Module 1-4
Midterm Examination Instruction:
- Students have to answer 10 questions among 12 questions.
- Each question contains 2.5 marks. So midterm examination is out of 25 marks.
- Time is 1 hour 30 minutes.
Midterm Preparation
- Discuss with each other and find the problems regarding upcoming midterm examination
- Try to solve the problems of each other
- If you have any problems that you can not solve, then inform me and we will discuss it in the classroom.
-
Lecture Contents:
- Types of yeast
- morphology
- reproduction and physiology
- pathogenic yeasts.
Lecture outcomes:
- Describe the types and morphology of yeast
- Compare and contrast between three types of yeast reproduction process
- Identify the pathogenic yeast with disease types
- Discuss about the advantages specially culinary use of yeast.
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

Lecture Contents:
- Introduction
- characteristics of rickettsiae
- pathogenic rickettsiae
- laboratory diagnosis of rickettsial diseases.
Lecture outcomes:
- Explain the characteristics of Rickettsiae
- Identify different pathogenic Rickettsiae
- Compare among different rickettsial disease
- Describe the diagnosis and treatment approach of this disease.
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

- The topic of presentation will be informed later
- The topic of presentation will be informed later
-
Lecture Contents:
- Virus inhibition
- human and animal viruses
- control of viral infections
- bacterial virus or bacteriophages
- morphology and composition
- cultivation of bacterial viruses
- reproduction of bacterial viruses.
Lecture outcomes:
- Describe the structure and shape of virus
- Distinguish between lytic and lysogenic cycle
- Explain the mechanism viral infection in host body
- Describe about bacteriophage
- Evaluate the difference between bacteriophages and virus
- Identify and describe different types of viral diseases
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-
Lecture Contents:
- Infections
- pathogenicity and virulence
- Active and passive immunity.
Lecture outcomes:
- Identify the component of immune system
- Distinguish between Innate and adaptive immune system
- Explain the interaction between antigen and antibody
- Describe the pathogenicity and virulence
-
Please try out this interactive quiz to judge your learning from this chapter before moving forward
-

Final Exam includes: Lecture Module 5-8
Semester Final Examination Instruction:
- Students have to answer 10 questions among 12 questions.
- Each question contains 5 marks. So semester final examination is out of 50 marks.
- Time is 2 hour 30 minutes.
- Discuss with each other and find the problems regarding upcoming midterm examination
- Try to solve the problems of each other
- If you have any problems that you can not solve, then inform me and we will discuss it in the classroom