Section outline
-
Welcome to Inorganic Pharmacy II Practical
Course Introduction:
This subject deals with the knowledge of Inorganic chemistry to identify inorganic compound and their test for identification and to explain the preparation methods of inorganic pharmaceuticals and their application in pharmacy.
Course Objectives:
Explain how to calibrate all the glassware and correct use of various types of equipment & Safety measures in Pharmaceutical Chemistry laboratory.
Able to perform limit tests
Application of limit tests
Explain how to identify the inorganic compound and their test for identification
Explain the preparation methods of inorganic pharmaceuticals and their application in pharmacy
Learning Outcomes:
After completing this course, students will be able to:
- Differentiate between different inorganic and organic compounds
- Explain how to calibrate all the glassware and correct use of various types of equipment & Safety measures in Pharmaceutical Chemistry laboratory
- Able to convert insoluble inorganic compound into a soluble compound
- Should be able to explain the preparation methods of inorganic pharmaceuticals and their application in pharmacy

Course Teacher
Sabreena Chowdhury Raka
Assistant Professor
Department of Pharmacy
Faculty of Allied Health Sciences
Contact No.: 01676-033062
Email: raka.pharmacy@diu.edu.bdWebsites: ORCID iD | Lab Site | Faculty Site | ResearchGate | Google scholar |
-
A short guideline on how to utilize this course in BLC.
-
General news and announcements
-
-
1. Introduction to Modern Inorganic Chemistry- S. Z. Haider, 1994, Friends International.
2. Modern Inorganic Chemistry- Madan, 1st (reprint 1997), S. Chand & Company Ltd.
3. Introduction to Modern Inorganic Chemistry- J. D Lee, 5th edition, Blackwells.
4. Bentley and Driver’s Textbook of Pharmaceutical Chemistry- Bently, Arthur Owen, 8th edition, Oxford University Press.
5. Modern Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry- Clarence A. Discher, Leonard C. Bailey, Thomas Medwick, 2nd edition, Waveland Pr Inc.
6. Rogers Inorganic Pharmaceutical Chemistry- Rogers, Charles Herbert, Taito O. Soine and Charles O. Wilson, 7th edition, Philadelphia, Lea &Febiger.
7. Inorganic Medicinal & Pharmaceutical Chemistry- Block, John H., Roche, Edward B., Soine, Taito O., Wilson, Charles O, 1974, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia.
8. R. Hendrickson et. al.(ed) Remington: the Science and Practice of Pharmacy. Twenty first edition. Lippincott Williams &Wilkins, Philadelphia, USA. 2005.
-
Experiment Name: Conversion of water insoluble benzoic acid to water soluble sodium benzoate.Principle:
Water is polar molecule. It dissolved only polar solid. In pharmaceuticals, Polarity increment may be required during several operations like liquid dosage form preparation. Increment is done by addition of polar salt or base with various non -polar substance. Increase the solubility of the solution with water.
Benzoic acid helps prevent infection caused by bacteria. Benzoic acid is a topical medicine used to treat skin irritation and inflammation caused by burns, insect bites, fungal infections, or eczema .The salt and esters of benzoic acid are known as benzoates.
Reaction:
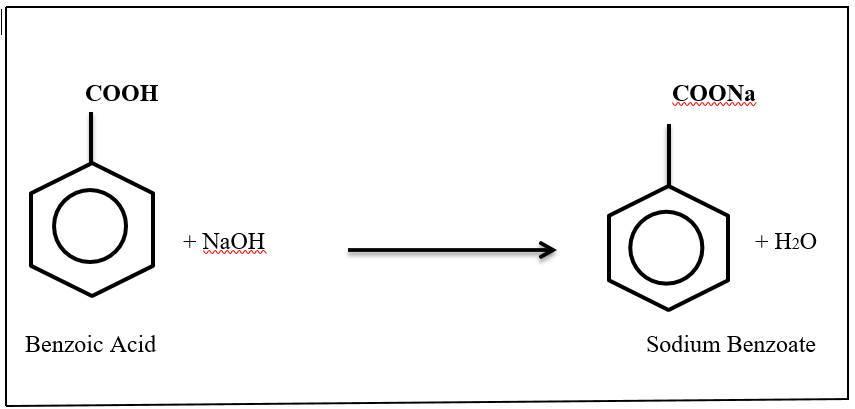
Figure 1: Benzoic acid with reacted sodium hydroxide and given product of sodium benzoate.
Required reagent for the experiment:
Ø Benzoic acid
Ø Sodium hydroxide
Ø Distilled water
Required apparatus for the experiment:
Ø Test tube
Ø Dropper
Ø Watch glass
Procedure:

Figure 2: All substance mixed in the test tube
01. Take small amount of Benzoic acid powder (< 0.5 gm).
02. Add small amount of H2O (approximately 1 ml ) and shake
03. Observe that the powder is not Dissolving.
04. Now added small amount of NaOH And shake well.
05. Observed that it dissolve the benzoic acid.
Result:
Water soluble sodium benzoate was observed.
Comment:
Benzoic acid was insoluble in water. It was added with sodium hydroxide. It produced sodium benzoate which was soluble in water.
Precautions:
Ø Have to wear laboratory apron, hand gloves, mask & goggles.
Ø Have to wear shoes during the experiment.
Ø Have to be very careful during the experiment.
-
Video Demonstration of Experiment 1
-
Conversion of water-insoluble Benzoic acid into water-soluble Sodium Benzoate
-
-
Experiment Name: Conversion of water-insoluble Salicylic acid into water Sodium Salicylate.
Principle:
Water is a polar molecule. It dissolved only polar solid. In pharmaceuticals, a Polarity increment may be required during several operations like liquid dosage form preparation. The increment is done by the addition of polar salt or base with various non-polar substances. Increase the solubility of the solution with water.
Salicylic acid topical is used in the treatment of acne, dandruff, seborrhea, or psoriasis, and to remove warts. Naturally, cucumber, broccoli, cauliflower, corn, radish, sweet potato, and fennel contain Salicylates.
Reaction:
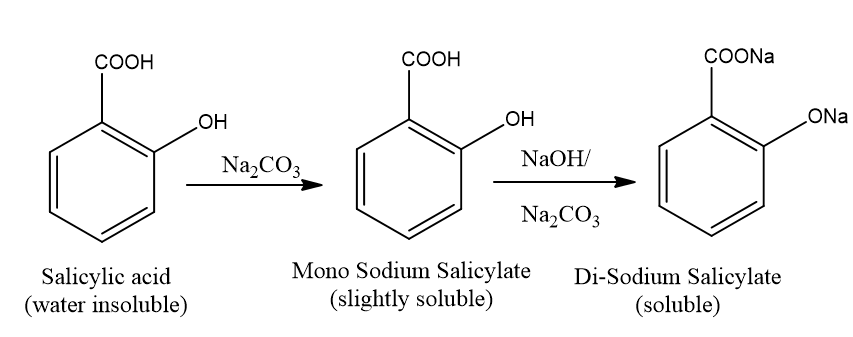
Fig. 2.1: Reaction between Salicylic acid and Sodium Carbonate.
Reagent:
§ Salicylic acid
§ Sodium carbonate
§ Distilled water
Apparatus:
§ 01.Test tube
§ 02.Dropper
Procedure:
01. Take a small amount of salicylic acid powder (< 0.5 gm).
02. Add a small amount of H2O (approximately 1 ml) and shake
03. Observe that the powder is not Dissolving.
04. Now added a small amount of NaCO3 and shake well.
05. Observed that it dissolves the Salicylic acid.
Observation:
Salicylic acid completely dissolved in the water due to the formation of Di-sodium Salicylate acid.
Result:
Salicylic acid-insoluble in the water but di-sodium salicylate soluble in the water
Comment:
Salicylic acid turned into di-sodium salicylate which was soluble in water
Precaution:
§ Have to wear laboratory apron, hand gloves, masks, shoes & goggles.
§ Have to be very careful during the experiment.
§ Wash apparatus with clean water.
-
Comnversion of water insoluble Salicylic acid into water soluble Di-sodium salicyalte
-
-
Assessment 1

-
-
Experiment Name: Qualitative test for known supplied a salt sample of Fe2+
Principle:
Each salt has two types of ions or radicals. One is cation from the basic part & another is an anion which comes from the acidic part. The basic part is positively charged & the acidic part is negatively charged. When the suitable reagent is added into the aqueous solution of a salt, the ions being precipitated and showed their own characteristics.
Reactions of Fe2+ solution:
1. Stock soln + NH3 [NH4CL + NH4OH ---------> white Fe(OH)2
2. Solution + NaOH --------> white ppt. of Fe(OH)2-------> Any acid soluble.
3. Solution + K4[Fe(CN)6 -------> white ppt. of K2Fe[Fe(CN)6].
4. Solution + NH4CNS ---------> Black ppt. of FeS --------> Soluble in acid.
Reagents:
· Stock solution
· Sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
· Potassium Ferro cyanide K4[Fe(CN)6
· Ammonium thiocyanate (NH4CNS)
Apparatus:
· Test tubes
· Dropper
· Measuring Cylinder
· Burner
Procedure:
At first prepare stock solution, then mix different reagents and used in different amount with the sample to be confirmed about the presence of Fe2+.
Observation No.
Test procedure
Observation
Result
01
Stock soln + NH3 [NH4CL+ NH4OH]
Dark blue Fe(OH)3 gelatinous
Fe2+ present
02
Stock soln + NaoH
White greenish ppt. of Fe(OH)2
Fe2+ Present
03
Stock soln + K4[Fe(CN)6
Light blue ppt.
K2Fe[Fe(CN)6].
Fe2+ Present
04
Stock soln + (NH4CNS)
No change
Fe2+ Present
Result:
Fe2+ present
Comment:
Dark blue, white greenish, light blue, no change precipitate confirmed the presence of Fe2+
Precaution:
- Need to wear an apron, hand gloves, masks, and goggles to protect eyes in the laboratory.
- Have to careful during the experiment.
- Hands must be washed before leaving the lab.
-
Test for Ferrous ion
Test 1: NH4CNS
Test 2: NaOH
Test 3: Potassium ferricyanide
-
Name of the Experiment: Qualitative test for known supplied salt sample of Fe3+.
Principle:
Each salt has two types of ions or radicals. One is cation which comes from the basic part & another comes from the acidic part. The basic part is positively charged & the acidic part is negatively charged. When suitable reagent is added into the aqueous solution of a salt, the ions being precipitated and showed their own characteristics
Reaction of Fe3+ solution:
1. Stock solution + NH3 [NH4Cl + NH4OH] à Brown Fe(OH)3 gelatinous ppt. + acid soluble.
2. Stock solution + NaOH à Brown ppt. of Fe(OH)3 à Any acid soluble.
3. Stock solution + K4[Fe(CN6)] à Dark blue.
4. Stock solution + NH4CNS à Black ppt. of FeS à Soluble in acid.
Reagents:
§ Stock solution.
§ Ammonia (NH3).
§ Sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
§ Potassium ferro cyanide K4[Fe(CN6)].
§ Ammonium thiocyanate (NH4CNS).
Apparatus:
§ Test Tube.
§ Dropper.
§ Measuring Cylinder.
§ Burner.
§ Glass rod.
Procedure:
At first prepare stock solution then mix different reagents and used in different amount with the sample to be confirmed about the presence of Fe3+.
Observation No.
Test procedure
Observation
Result
01.
Stock solution + NH3 [NH4Cl + NH4OH]
1. Brown Fe(OH)3 gelatinous ppt. + acid soluble.
Fe3+ present
02.
Stock solution + NaOH
Brown ppt. of Fe(OH)3
Fe3+ present
03.
Stock solution + K4[Fe(CN6)]
Dark blue
Fe3+ present
04.
Stock solution + NH4CNS
Black ppt. of FeS
Fe3+ present
Result:
Fe3+ present.
Comment:
Brown gelatinous ppt, Brown ppt, dark blue and black color precipitate confirmed presence of Fe3+
Precaution:
- Wear lab apron properly.
- Wear hand gloves.
- Take all the reagents carefully.
-
Test for Ferric ion
Test 1: NH4CNS
Test 2: NaOH
Test 3: Potassium ferricyanide
-
Assessment 2

-
-
Experiment Name: Preparation of Aluminum Hydroxide Al(OH)3 gel
Principle:
Aluminum is a naturally occurring mineral. Aluminum Hydroxide is an antacid. Antacids are the oldest effective medications for heartburn. Most commercially available antacids are combinations of aluminum and magnesium hydroxide. Some effervescent antacids contain sodium bicarbonate. This medication is used to treat the symptoms of too much stomach acid such as stomach upset, heartburn, and acid indigestion. Aluminum Hydroxide works quickly to lower the acid. Liquid antacids usually work faster than tablets or capsules.
Aluminum Hydroxide Al(OH)2 is a suspension, 100 mg of which contain the equivalent of 3.6-4.4 gm of Aluminum Oxide (Al2CO3) in the form of Aluminum Hydroxide & Hydrate Oxide. Sodium Carbonate (Na2CO3) reacts with potash alum and produce water-insoluble viscous Aluminum Hydroxide gel.
Reaction:
Al2(SO4)3 + 3Na2CO3 + 3H2O = 2Al(OH)3 + 3Na2SO4 + 3CO2
Reagents:
§ Sodium Carbonate (Na2(CO3)
§ Hot water
§ Potash alum [KAl(SO4)2]
Apparatus:
Beaker
Glass Rod
Filter paper
Pipette
Funnel
Procedure:
1. We measured 0.5 gm Na2CO3 & 1.5 gm Potash alum in wo separate beakers.
2. Then we added 25 ml hot water at each beaker.
3. Potash alum solution was also added to the hot solution of Na2CO3. A white precipitation of Al(OH)3 is formed.
4. Then we filtered the precipitated aluminum hydroxide to find aluminum hydroxide gel.
Result:
Al(OH)3 formed
Comment:
The white-colored Al(OH)3 gel was formed
Precaution:
§ Have to wear laboratory apron, hand gloves, mask & goggles.
§ Have to wear shoes during the experiment.
§ Have to be very careful during the experiment.
§ Have to take all reagents carefully.
-
Preparation of Al(OH)3 Gel
-
Experiment Name: Qualities analysis of known supplied a salt sample of Al3+
Principle:
Each salt has two types of ions or radicals. One is a cation that comes from the basic part & another is an anion that comes from the acidic part. The basic part is positively charged & the acidic part is negatively charged. When the suitable reagent is added into the aqueous solution of a salt. The ions being precipitated show their own characteristics
Required Reagents for the experiment:
1. Stock Solution
2. Sodium Hydroxide ( NaOH )
3. Ammonium Hydroxide ( NH4OH )
4. Ammonium Chloride ( NH4Cl )
5. Al2Cl3
Required apparatus for the experiment:
Ø Test tubes
Ø Dropper
Ø Measuring Cylinder
Ø Burner
Ø Test tube holder
Ø Glass rod
Procedure:
At first prepare stock solution, then mix different reagents and used in different amount with the sample to be confirmed about the presence of Al3+
Observation No.
Test procedure
Observation
Result
01
Stock soln +NaOH
+Heat
White/brown ppt
Al3+ present
02
Stock soln +NH4OH
+NH4Cl
White gel of
Al(OH)2 formed
Al3+ present
Result:
Al3+ is present
Comment:
After adding NaOH the white color ppt confirmed the presence of Al3+ in the supplied sample.
Precaution:
· Have to be very careful during the experiment.
· Have to wear a laboratory apron, hand gloves, mask & goggles.
· Have to wear shoes during the experiment.
-
Test for Al3+ ion
-
-
-
-
-
Final Submission Date: 2 May 2021 (11:59 PM)
Format: pdf file
Total Marks: 20 Marks
Good Luck!!