Section outline
-
-

I welcome all of my beloved students to the Computer Graphics course!!!. Computer Graphics is the major field of Computer Science & Engineering, which is the order of originating images with the computer. It's a core technology in digital photography, video games, film, cellphone & computer displays as well as many specialized applications. Hope our journey will be nice together. Enjoy your learning.
Regards,
Instructor: Md Montasir Bin Shams
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 1: Introduction to Computer Graphics
Lecture 2: Video Display Devices: Refresh Cathode Ray Tubes, Raster & Random Scan displays, Color CRT Monitors, DVST & Flat panel displaysExpected Learning Outcome:
- Appreciate the use of Computer Graphics and it's real-life application.
- Able to explain the core concepts of computer graphics, including output primitives, anti-aliasing, transformation, and viewing in 2D.
Book Chapter
Chapter 1: A survey of Computer Graphics
Chapter 2: Overview of Graphics SystemContents
1.Introduction to Computer Graphics (PPT)
2.Audio File(8MB) Introduction to Computer Graphics
Write your feedback after every class:
-
How plasma display perform?
-
Currently which display deceives do you use? Mention some of the features of the display that you like most and limitations also that you faced.
-
Feel free to ask any question regarding this week's lesson
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 3: Points and Lines, Line drawing Algorithm
Lecture 4: DDA Algorithm- example with a plot in a graphExpected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 3: Output Primitives
Write your feedback after every class:
Click here for the feedback...
-
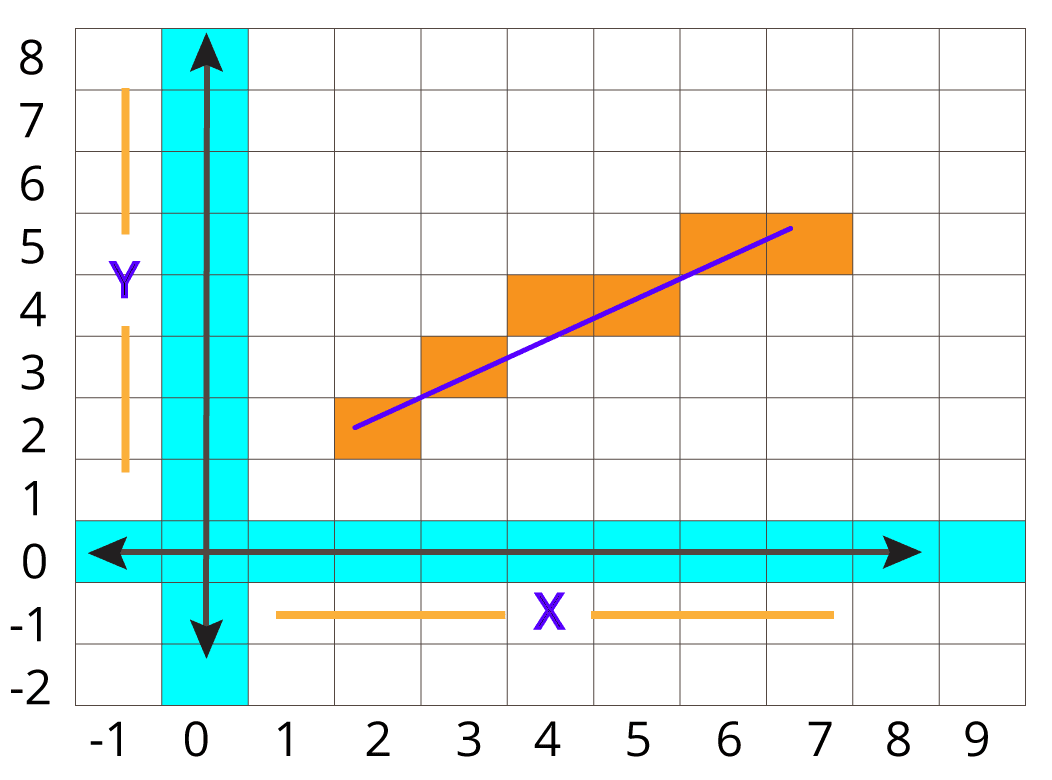
Suppose you have given two endpoints (-2,-7) and (3,3). Draw the line using the DDA algorithm.
N.B: You have to solve the problem in a reversed way, i.e goes from top point to bottom point.
-

Topics for discussion
Class Test 1
Lecture 5: Parameter Description of Bresenham Line Drawing Algorithm
Lecture 6: Bresenham Line Drawing Algorithm Implementation with ExampleExpected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 3: Output Primitives
-
Feel free to ask any question regarding this week's lesson
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 7: Properties of Circle, Circle Drawing Algorithm: Midpoint
Lecture 8: Midpoint circle drawing Algorithm Implementation
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 3: Output Primitives

-
Feel free to ask any question
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 10: Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformation
Lecture 11: Review Class (Previous Lecture)
Presentation Announcement
Expected Learning Outcome:
- To evaluate the transformation of an object and viewing in two dimensional way..
- To perform with the mathematical expression in a computational display.
Book Chapter
Chapter 5: Two-Dimensional Geometric Transformation

-
Mid Term Syllabus:
1. Application of Computer Graphics
2. Video display devices
3. Line Drawing Algorithm (DDA, Bresenham)
4. Circle algorithm.(Mid Point)-
Dear students,
Before the exam please read out the exam guidelines carefully. You have to submit your answer scripts both in BLC and google form( Will be provided in the Telegram group) in due time.
-

Topics for discussion
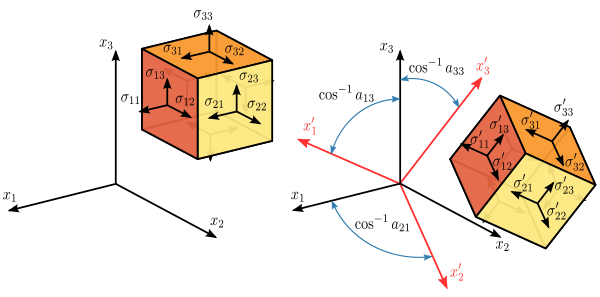
Lecture 19: 3D Geometric Transformation
Presentation
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 11: Three-Dimensional Geometric & Modeling Transformation
-
Dear Learner,
Hope you are within fantastic journey of the learning. Now it's time to show your spark. Submit your presentation in the following thread.
Best Wishes..
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 12: Two-Dimensional Viewing, Window-to-Viewport Coordinate Transformation
Lecture 13: Two-Dimensional Clipping, Line Clipping Algorithm: Cohen-Sutherland
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 6: Two-Dimensional viewing
-

Topics for discussion
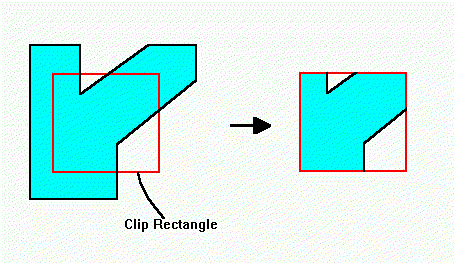
Lecture 14: Two-Dimensional Clipping, Polygon Clipping Algorithm: Sutherland Hodgeman- Example
Lecture 15: Two-Dimensional Clipping, polygon clipping Clipping Algorithm: Weiler Atherton - Example
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 6: Two-Dimensional viewing
-

Topics for discussion
Lecture 16: Two-Dimensional Clipping, Polygon Clipping Algorithm: Sutherland Hodgeman
Lecture 17: Two-Dimensional Clipping, polygon clipping Clipping Algorithm:
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 6: Two-Dimensional viewing
-

Topics for discussion
lecture 18: Three Dimensional Display Methods, Parallel Projection, Perspective projection
Lecture 19: Depth Cueing, Visible Line and Surface Identification, Surface Rendering
Expected Learning Outcome:
- Able to understand the core concept of output primitives and transformation.
- Able to implement the algorithm rendering the graphics.
Book Chapter
Chapter 9: Three Dimensional Concepts
-
Final Exam Syllabus:
1. Transformation-2D and 3D (Five Basic Operations with example)
2. Viewing: Window to viewport mapping
3. Clipping- Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping Algorithm, Polygon Clipping Algorithm: Sutherland Hodgeman, Weiler-Atherton Polygon Clipping Algorithm.
4. 3D Display: Parallel and perspective projection, Depth Cueing (Definition), Surface rendering (Definition)-
Instructions for Submitting:
***you all have to submit your answer scripts in both BLC and google form.
*** Students have to submit their answer scripts in a specific format in google forms[Instructions regarding file naming is provided on the top of google form with examples]
Google form link: