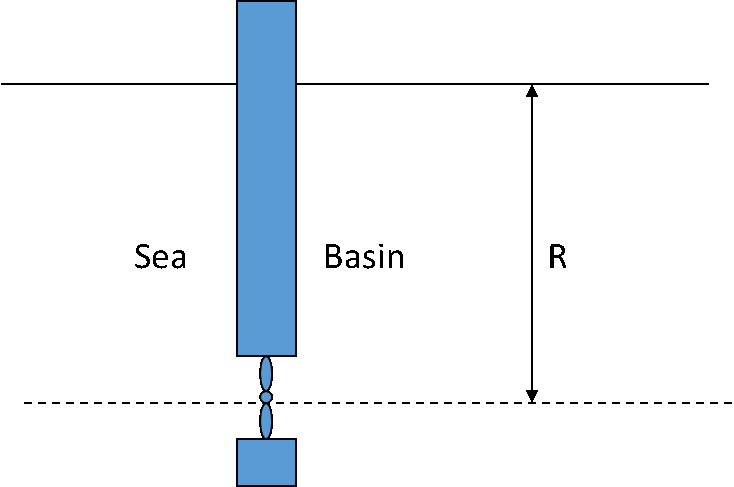Section outline
-
-
What is an Environment?
Simply said, an environment is a system made up of all biotic and abiotic elements that have an effect on human life. All types of flora and fauna are categorized as biotic, or living, elements, in contrast to the abiotic categories of water, sunlight, air, climate, etc.
Any product, service, or element that benefits people and society can be categorized as an environment's resource. Anything that satisfies a person's daily needs qualifies as one of them. Food produced by living things and plants, energy used for heating and cooking, wind, and oil are only a few examples of environmental resources.
Numerous products and services that are necessary to sustain life are provided by the environment. Each resource is priceless and holds a particular amount of significance. A piece of land might be turned into a park, a housing complex, a retail space, etc. Additionally, it can be used as a trash container.
-
-
-
-
Earth’s Hydrospheric Natural Resources
Hydrosphere is the sphere of water. It encompasses the global water resources and its distribution over the land, atmosphere, and oceans. The water resources of the globe include, the major oceans and seas, glaciers and ice on mountains and polar regions,. Rivers and streams with their running water Lakes, ponds and reservoirs Groundwater and soil moisture and the water vapour.
The major part of the global water is saline and is present in the oceans. Fresh water is very limited and is found in rivers and in lakes. The surface water resources are mainly used for-
· Drinking and sanitation
· Agriculture and irrigation
· domestic consumption
· industrial processes
· power generation
· water transport.
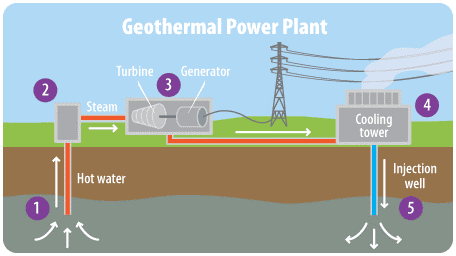
Groundwater resources are mainly used for drinking, domestic consumption and industrial applications when the surface water is limited.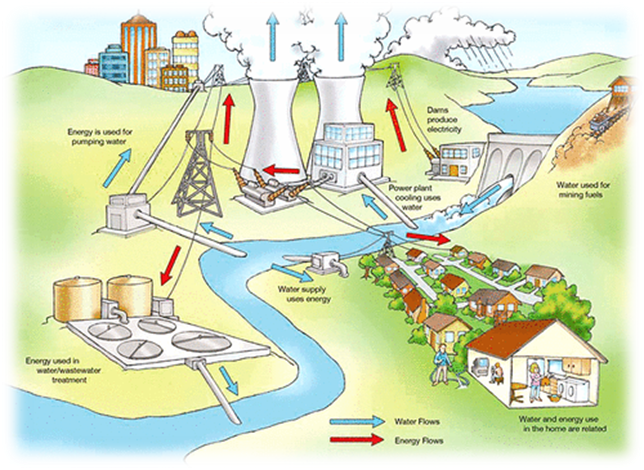
-
-
-
Impacts of Resource on Economy
- Most of the resources that are useful somehow possesses economic values.
- Diamonds, Rocks and other Minerals, Mountain stones, Mines, Energy can be good examples.
- Resource economics is one of the key to their management.
Human well-being is dependent on natural resources. Our survival without clean air, plants, and drinkable water is simply impossible. At the same time, some natural resources that are not vital in the way that water is, are still highly important for our survival. Oil, coal, and copper are just a few of the commodities that planet Earth offers us.
-
-
-
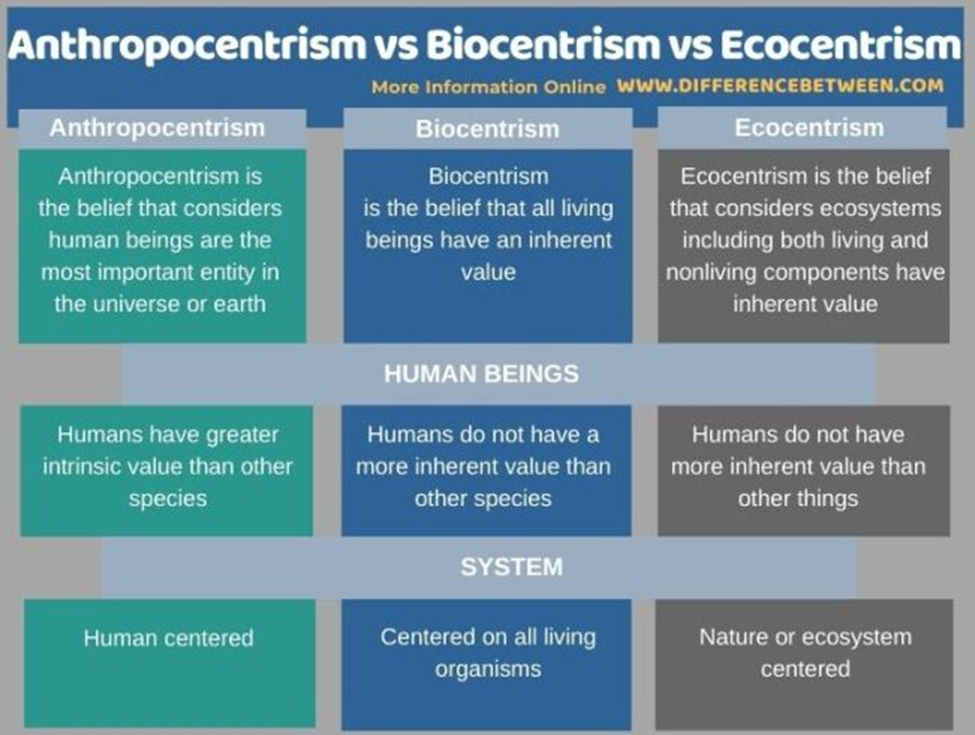
Ecological Footprint
ecological footprint (EF), measure of the demands made by a person or group of people on global natural resources. It has become one of the most widely used measures of humanity’s effect upon the environment and has been used to highlight both the apparent unsustainability of current practices and the inequalities in resource consumption between and within countries.

-
-
-
Wildlife Management
Wildlife management is the art and science of reaching goals by manipulating and/or maintaining wildlife habitats and populations. Wildlife management aims to halt the loss in the Earth's biodiversity by taking into consideration ecological principles such as carrying capacity, disturbance and succession, and environmental conditions such as physical geography, pedology and hydrology. Most wildlife biologists are concerned with the conservation and improvement of habitats; although re-wilding is increasingly being undertaken. Techniques can include reforestation, pest control, nitrification and de-nitrification, irrigation, coppicing and hedge laying.
-
-
-
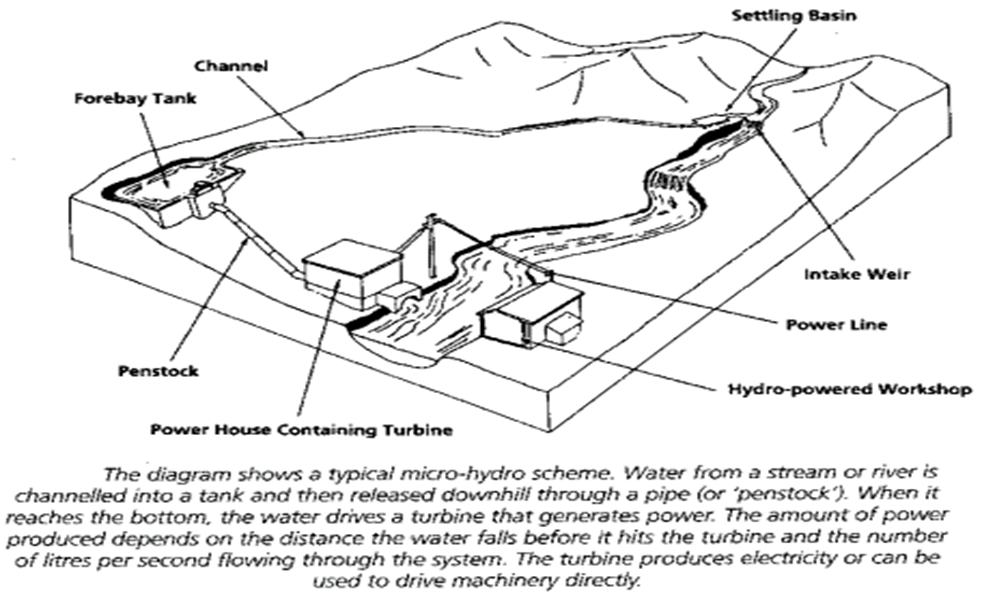
Hydropower
Hydropower is the electricity, generated by using the potential and kinetic energy of Water. Hydropower, or hydroelectric power, is one of the oldest and largest sources of renewable energy, which uses the natural flow of moving water to generate electricity. Hydropower, also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a water source to produce power. Hydropower is a method of sustainable energy production.
-
-
-
-
-
Opened: Wednesday, 1 November 2023, 12:00 AMDue: Sunday, 5 November 2023, 11:00 PM
Submit your homework handwritten pdf
-