Course Introduction:
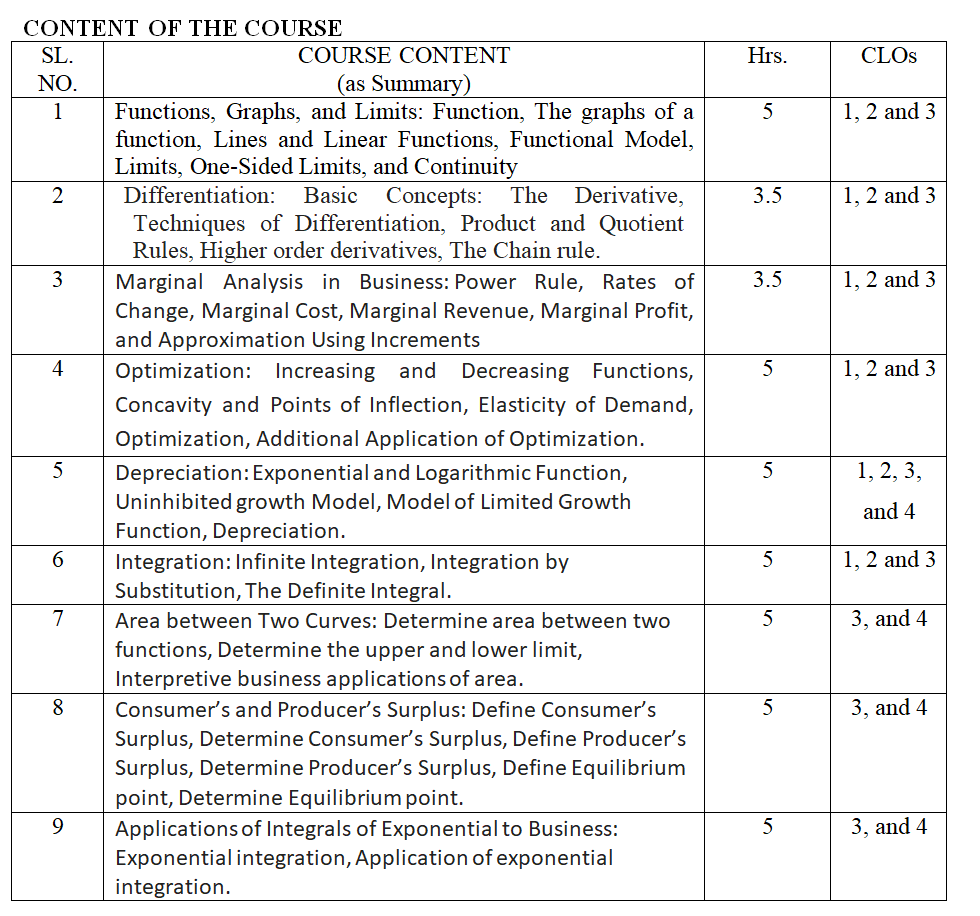
An introduction to differential and integral calculus, with an emphasis on applications, designed primarily for business, economics, and social sciences. Topics include limits, the first and the second derivative, the first and second derivative tests for relative extrema; exponential and logarithmic functions; the definite and indefinite integral, and the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Calculus will be used to solve real world applications.
Course Objectives:
By
the end of the course, student will be able to:
- Remembering and Understand
the rules of differentiation in different functions,
rules of integration in a different function, Optimization method using
differentiation, uninhibited growth model, model of limited growth function,
depreciation using differentiation, a method to find the area of space,
consumers’/producers’ surplus using integration.
- Apply the knowledge of rules of differentiation, rules of integration,
Optimization method, uninhibited growth model, model of limited growth function,
depreciation, a method to find the area of space, and consumers’/ producers’
surplus using integration to solve problems.
- Analyze the knowledge of optimization method, uninhibited growth model, model
of limited growth function, depreciation, a method to find the area of space,
and consumers’/ producers’ surplus using integration to make an effective
business decision.
Course Outcomes:
Students will:
ü Differentiate algebraic, exponential and logarithmic
functions, including use of product, quotient, generalized power and chain
rules.
ü Solve application problems from business and economics
involving graphing, minimization and maximization and economic lot size using
differentiation.
ü Integrate functions using the basic rules of
integration and substitution.
ü Solve application problems from business and economics
involving area, consumer’s surplus and producer’s surplus.
ü Find first and second order partial derivatives for
algebraic, exponential and logarithmic functions.
ü Solve maximization and minimization problems using
partial derivatives.